Dr. Youngran Park
Dr. Youngran Park
Dr. Park received her Ph.D. in Pathobiology from Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and is currently a postdoctoral research fellow at JHU. She received Pathology Young Investigator Day Award at 2016 and 2017 for her study of ARID1A function in DNA repair. She strongly believes the spirit of translational research is to alleviate human suffering through research.
Awareness is the first step toward endometriosis treatment
We want to reiterate the importance of endometriosis, by handling the paper entitled "Endometriosis awareness: screaming at the top of our voices" published on April 2021 in the journal “Women & Health”. The Endometriosis Awareness Month of 2021 was a little different, due to the pandemics. According to Dr. Ferreira and Dr. Carneiro, from the Federal University of Minas Gerais, Brazil, "it never stresses enough the importance of acknowledging this condition". Worldwide, at least 10% of women have endometriosis, and 50% of…
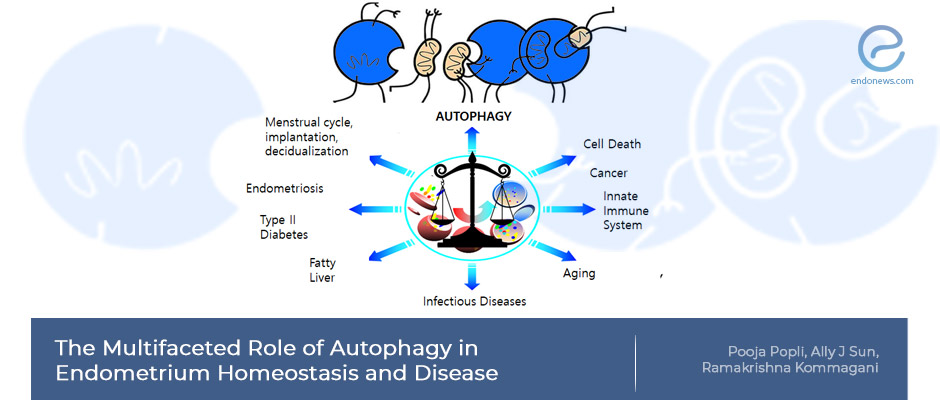
Key Points Lay SummaryAutophagy, Endometrium and Endometriosis
Autophagy, or autophagocytosis, is a self-digestion process by which cells recycle non-functional proteins to repurpose them. Unwanted cellular parts in cytosolic material are first isolated within double-membrane vesicles called the autophagosome, which subsequently fuses with the acidic lysosome. Autophagy is a survival mechanism, conserved across species, and is essential for maintaining endometrial homeostasis and mediating endometrial-specific functions, including menstrual cycle, embryo implantation, and decidualization. Studying the role of autophagy in the endometrium will provide a better understanding of its pathophysiology and offer…
Key Points Lay SummaryCan we measure the severity of endometriosis?
Endometriosis is an enigmatic disease associated with serious morbidity and change in the quality of life. Unfortunately, there is no specific test for the diagnosis of endometriosis. While many markers were evaluated in many research studies for the noninvasive diagnosis of disease including CA125, none were revealed to be of great benefit. Leptin is a protein and a product of the ob(obesity) gene. This hormone has a role in basal metabolism, reproduction, and food intake. Leptin also has immune-regulatory, proinflammatory,…
Key Points Lay SummaryErastin, Ferroptosis and Endometriosis
Iron overload has been linked to endometriosis. There are abundant free iron and high oxidation in ectopic lesions, probably due to retrograde menstruation. Interestingly, iron overload in endometriosis activates NF-kB signaling and results in proinflammatory communication. More clear pieces of evidence support that the imbalance of iron homeostasis enhances endometriosis development. Ferroptosis is characterized by iron-dependent, lethal lipid peroxidation accumulation. This iron-dependent cell death is found to be triggered by a small molecule named "erastin". Until now, the effect of…
Key Points Lay SummaryThe influence of endometrioma and surgery on ovarian reserve
Women with endometriosis and endometrioma, often have subfertility. These patients present considerable problems for the evaluation of ovarian reserve. One of the well-known ovarian reserve biomarkers is anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) levels. So far, it was known that the reduction of serum AMH level is associated with endometrioma, which destroys the normal ovarian tissue. Also, surgical removal of endometrioma was thought to reduce ovarian reserve and AMH levels. Contrary to this view, several recent studies present opposite results. To understand their…
Key Points Lay SummaryDNA damage response in eutopic endometria of endometriosis patients
The DNA damage response (DDR) is a network of cellular pathways that sense, signal, and repair the lesions occurring in DNA. Surveillance proteins that monitor DNA integrity activate the DNA repair pathways in response to DNA damage and try to prevent the generation of potentially deleterious mutations. Endometriosis is an estrogen-dependent disorder. Molecular mechanisms for the development of endometriotic lesions in a variety of extra-uterine sites have been widely examined. Similar to those of cancer cells, endometriosis tissues show higher susceptibility to DNA damage due to high oxidative stress and accumulate…
Key Points Lay SummaryNanomedicines for Endometriosis
Scientific research on nanoparticles is intense as they have many potential applications in medicine. Nanomaterials have been widely explored for imaging and treatment of various diseases, especially cancer, over the recent twenty years. The absence of non-invasive diagnostic tests and inability of definitive diagnosis without gold-standard laparoscopic surgery, endometriosis patients face long diagnostic delays. Furthermore, diminished quality of life and disrupted fertility by medical hormonal therapies are the main reasons for the growing requirement of efficient non-surgical strategies for the diagnosis…
Key Points Lay SummaryGenetic and Pathologic aspects of Maligant Transformation of Endometriosis: Endometriosis-Related Ovarian Cancers-ERON's - Ayse Ayhan, MD
In the 2020 Endofound Medical Conference, Dr. Ayse Ayhan presented about endometriosis (endometrioma)-related ovarian cancer (ERON). Based on the current understanding of the epidemiology, histology, and molecular alterations, it seems clear that endometriosis is highly related to ERONs. Endometriosis is highly associated with ovarian cancer incidence. Especially in Asia areas, there is a 4-fold increase of ovarian cancer incidence in endometriosis patients compared to the control. ERONs, which include clear cell ovarian carcinoma, endometrioid ovarian carcinoma, seromucinous borderline tumors, are…
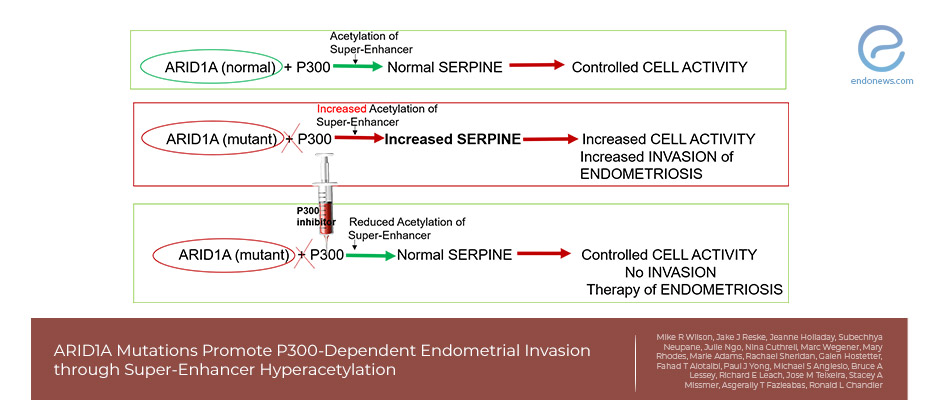
Key Points Lay SummaryA Possible genetic target for endometriosis treatment
Mutations in the chromosome remodeling complex SWI/SNF subunit ARID1A were first identified in ovarian clear-cell carcinoma and ovarian endometrioid carcinoma, two endometriosis-associated epithelial ovarian cancer subtypes. ARID1A gene mutations are also observed in deep ovarian and deep infiltrating endometriosis, atypical endometrial hyperplasia, and endometrial cancer. These mutations may increase the risk of endometriosis and malignant transformation by providing a selective advantage to displaced endometrial cells. In this paper, Dr. Chandler's group identifies a mechanism by which ARID1A represses invasive phenotypes by…
Key Points Lay SummaryPain in Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a chronic and debilitating condition characterized by chronic pelvic pain (CPP) and infertility. It affects approximately 10% of women globally and more than 60% of women diagnosed with endometriosis report CPP. However, the mechanisms underlying the associated pain remain poorly understood. In this review, Dr.Brierley group from Australia summarizes the most recent clinical and preclinical research to highlight advances in determining the mechanisms underlying the development of endometriosis-associated CPP and chronic abdominal pain. This paper was recently published in…
Key Points Lay SummaryEndometriosis and Natural Killer Cell Immunity
It is known that approximately 25 to 50% of infertile women have endometriosis, and 30% to 50% of the women with endometriosis have infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss. Previous studies have shown that women suffering endometriosis have abnormal NK cell activity and abnormal expression of inhibitory receptors, suggesting immunological changes play a critical role in infertility or reproductive failure. Although several factors including retrograde menstruation, bacterial infections, and epigenetic factors play role in the development of endometriosis, one important factor is…
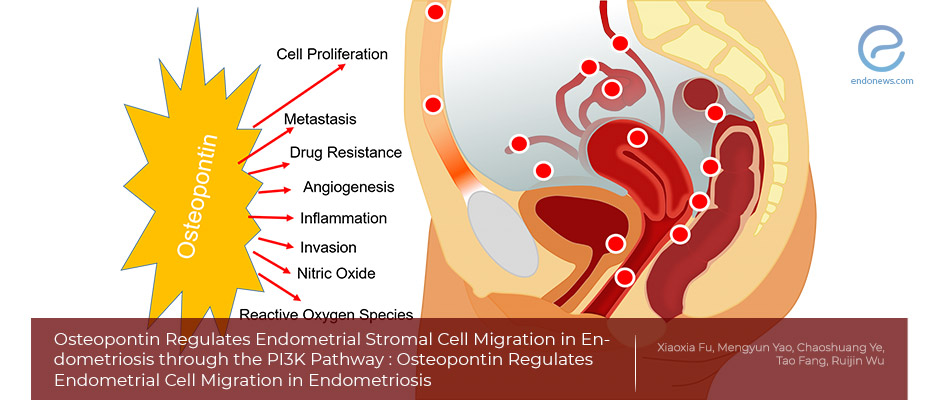
Key Points Lay SummaryOsteopontin and Endometriosis
Although characterized as a benign disease, some properties of endometriosis mimic malignant tissues such as proliferation, cell invasion, and metastasis. Osteopontin, also called secreted phosphoprotein 1, is one of the important molecular targets in cancer progression and metastasis. Osteopontin has been found in a variety of tissues including bone matrix, secretory glands, and some tumor tissues, and also secreted by activated immune cells. A previous study illustrates that Osteopontin is overexpressed in a wide range of malignant tumors including endometrial carcinoma, and…
Key Points Lay SummaryStem cell and exosome therapy
These days, two experimental methods, stem cell, and exosome therapy are getting more attention. Stem cell therapy has shown promising effects in regenerative medicine, including myocardial infarction, nervous system impairment, retinal damage, and liver diseases. Recent studies showed that stem cells could secrete nano-scale vesicles called exosomes. Exosomes are soluble, bi-layer nano-vesicle cargos, ranging from 30 to 150 nanometers. They are released from the naturally occurring late endosomes and contain different molecules such as enzymes, microRNAs, DNA fragments, lipids, and…
Key Points Lay SummaryCellular communications: Exosomes in Endometriosis
Exosomes have been reported as cell-to-cell communicators, transfer many molecules such as miRNAs, RNAs, and proteins, and their alteration may cause many disease processes, including endometriosis. Considering the role of exosomes and their cargos in a cell to cell communication as important factors in folliculogenesis and endometrial development, understanding of exosomes in the endometriosis context is highly important. Here, Dr. Yousefi group summarizes the recent reports of extracellular vesicles (EV) secreted by follicles and endometrium. This review paper is recently published in…
Key Points Lay SummaryAntioxidant Enzymes in Endometriosis
Recent attention has been focused on the effect of oxidative stress in the development of endometriosis. Especially, there are several studies regarding glutathione peroxidase (GPX), a major enzyme in removing various reactive oxygen species. In the field of infertility, the role of oxidative stress in recurrent miscarriages with unknown etiology has been investigated. The expression of glutathione peroxidase between eutopic and ectopic endometrial tissues is also different. Though several studies suggest the importance of GPX in endometriosis, it is currently…
Key Points Lay SummaryBowel surgery for endometriosis
Endometriosis is an estrogen-dependent disorder. The disease harbors various complications. Deep endometriosis involving the bowel is only one aspect of the condition that has variable phenotypic presentations and pathologic subtypes. Knowledge of the short- and long-term risks of the surgical management of endometriosis involving the bowel is a key competency for the surgeon and essential to help guide patients through the treatment process. However, the literature to date has inherent limitations that prevent generalizability. Here, Dr. Singh group from Canada…
Key Points Lay SummaryImmune cells and endometriosis pain
Endometriosis is an estrogen-dependent inflammatory disorder in women. This disease leads to dysmenorrhea, pelvic pain, and infertility. The immune reaction is one of the most widely accepted pathologies of endometriosis. Estrogen dysfunction stimulates immune cells in the peritoneal cavity affecting not only T & B lymphocytes, peritoneal macrophages, but also inflammatory mediators. In a previous study, M2 macrophages have been shown to play key roles in promoting endometriosis progression. Importantly, there is crosstalk among macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, and T…
Key Points Lay SummaryIncreased expression of epithelial cell adhesion molecule and its possible role in epithelial-mesenchymal transition in endometriosis.
Endometriosis is an estrogen-dependent disease that functional endometrial tissue exists outside both the uterine cavity and myometrium. The pathogenesis of endometriosis remains unclear and controversial. According to the implantation theory, which is the most well-known, migration and invasion are two critical processes for the development of endometriosis. Accumulating evidence demonstrated that endometriosis has mobile and invasive features. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) has been more attractive as one of the essential molecular mechanisms contributing to metastasis and invasion, which are critical for…
Key Points Lay SummaryLocal inflammation and follicle development in women with ovarian endometriosis
Endometriosis, a cause of subfertility, is found in almost 50% of infertile women. The elevated levels of cytokines in the follicular fluid of patients with endometriosis might account for the ovulatory dysfunction. Granulosa cells (GCs) play important roles in follicular development. In patients with endometriosis, abnormalities in GCs might impair oocyte maturation and lead to poor oocyte quality. Nuclear factor k B (NF-kB) was the key point in inflammation. Activated by inflammatory cytokines, NF-kB was involved in cascade signal amplification…
Key Points Lay SummaryRace, socioeconomic status, and health
Racial disparities in health have been long noted in the United States. The differences in socioeconomic status across racial groups are a major contributor to racial disparities in health. However, race reflects multiple dimensions of social inequality. Understanding and effectively addressing racial disparities in health requires an appreciation of the contributing factors that importantly affect the racial patterning of the distribution of disease. In this paper, Dr. Collins group provides an overview of recent research on racial disparities in health…
Key Points Lay Summary